Yuecheng Liu Win the Team Champion of L2RPN NIPS 2020 Competition During Internship at Baidu

Overview
Power grids transport electricity across states, countries and even continents. They are the backbone of power distribution, playing a central economical and societal role by supplying reliable power to industry, services, and consumers. Their importance appears even more critical today as we transition towards a more sustainable world within a carbon-free economy, and concentrate energy distribution in the form of electricity. Problems that arise within the power grid range from transient brownouts to complete electrical blackouts which can create significant economic and social perturbations, i.e.de facto freezing society. Grid operators are still responsible for ensuring that a reliable supply of electricity is provided everywhere, at all times. With the advent of renewable energy, electric mobility, and limitations placed on engaging in new grid infrastructure projects, the task of controlling existing grids is becoming increasingly difficult, forcing grid operators to do “more with less”. This challenge aims at testing the potential of AI to address this important real-world problem for our future.
Robustness Track
In this track, develop your agent to be robust to unexpected events and keep delivering reliable electricity everywhere even in difficult circumstances. An opponent, which we disclose to you, will attack in an adversarial fashion some lines of the grid everyday at different times (you can think of cyber-attacks for instance). You will have to overcome his attacks and keep operating the grid safely.
Solution
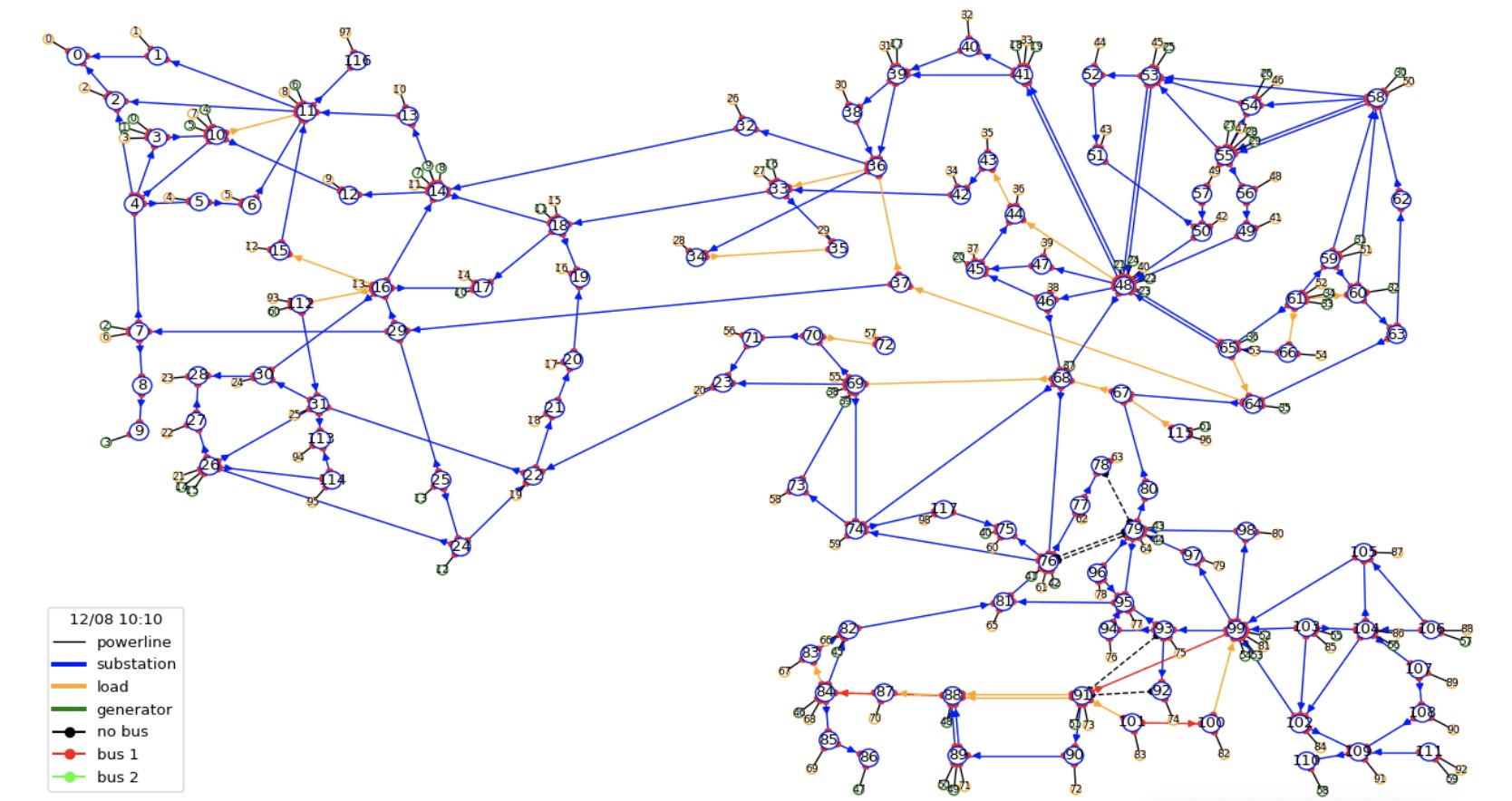
A direct challenge to apply existing machine learning methods is the humongous observation space and action space (including both discrete and continous action space). For example, to modify the topology of the power network, there are over 65000 actions avaible at every time step. To reduce the action space, a direct way is to traverse the whole action space and select the topN most effiective actions.
In most cases, the problem can not be solved in single step, and it is to greedy to directly select the best action at every single time step which will lead to suboptimal solution. In the power network, if a line keeps overflow over 3 steps, the line will breakdown. It would be better if we can tackle the problem in 3 steps after the overflow appeared, thus we could select some multi-step actions (3 step here). Some greedy based method are used to tackle the large action space (65000^3, over 200 trillion, omit the details here). After that a prediction model is constructed based on supervise learning to predict the max rho (max overflow rate) after 3 steps action after taking the actions.
We aslo utilize ES (Evolution Strategy) to improve the model. The ES algorithm take cumulative reward as the fitness function,
- correct the bias of the supervised model introduced by the label provided by the env simulator.
- obtain more benifit from the long-sight view.
We have also tried traditional reinforcement learning method (such as IMPALA and Ape-X), however, it is difficult for the model to capture the variation on the topology of the power network. To tackle the problem, Graph Neural Network (GNN) may be help, but not all kinds of GNNs (such as GCN) can be directly used since in the settings of L2RPN, taking actions may split the single node to two different nodes. In these cases, methods such as GAT may be help.
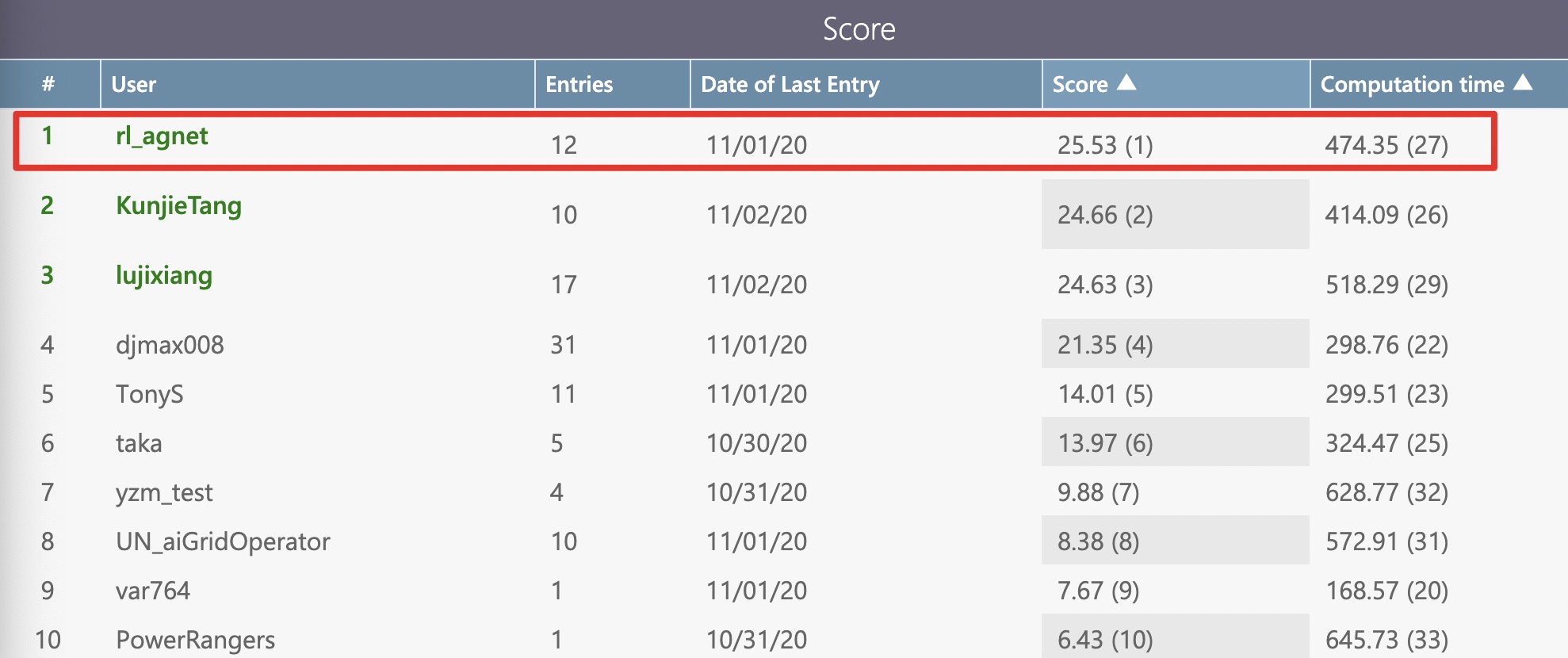
Score
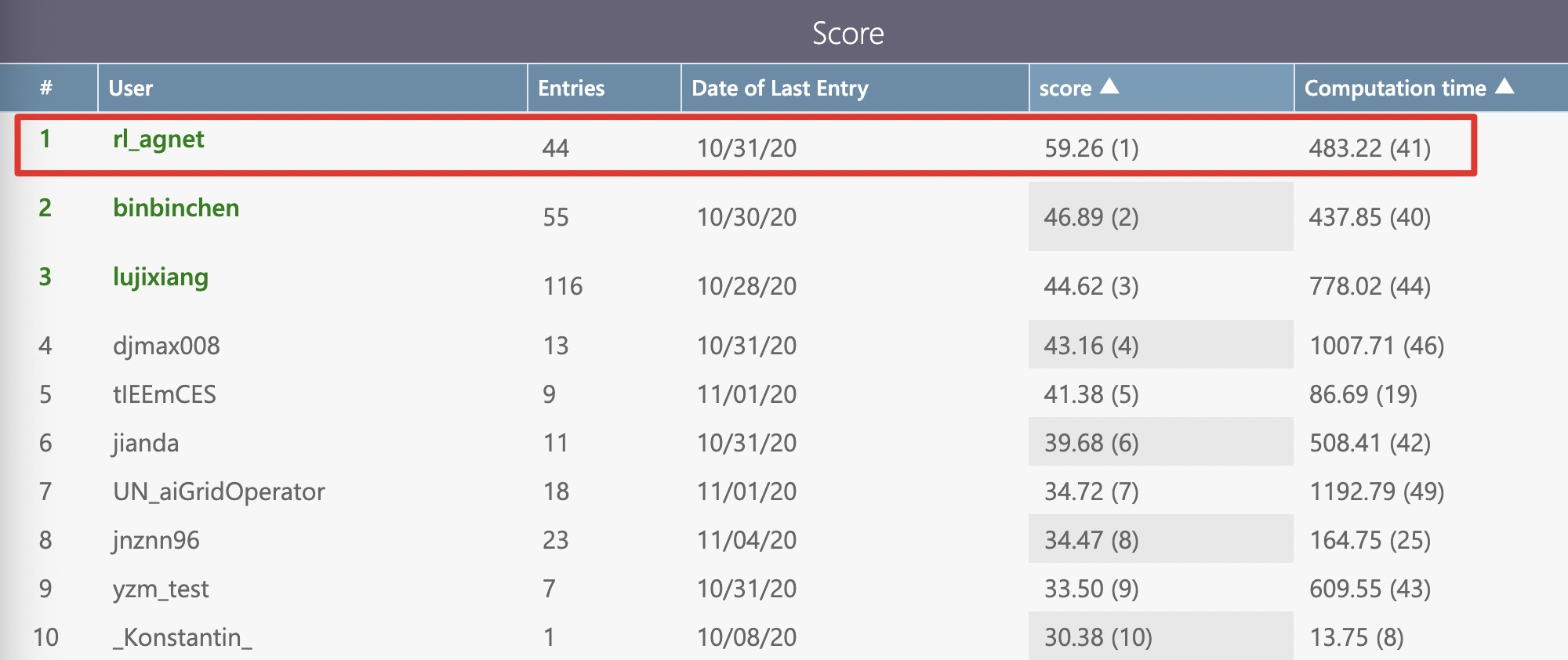
Adaptability Track
Score